ACCIONA's projects seek to have a positive impact on the planet through business models based on decarbonization, water and ecosystem conservation, and the circular use of resources.
POSITIVE PLANET
INVESTING TO REGENERATE THE PLANET
HIGHLIGHTS: 2021
- Reduced GHG emissions compared to base year 2017 by 19% (Scope 1 and 2) and 28% (Scope 3* categories in SBT), in line with the science-based target. Maintained carbon neutrality in its direct operations.
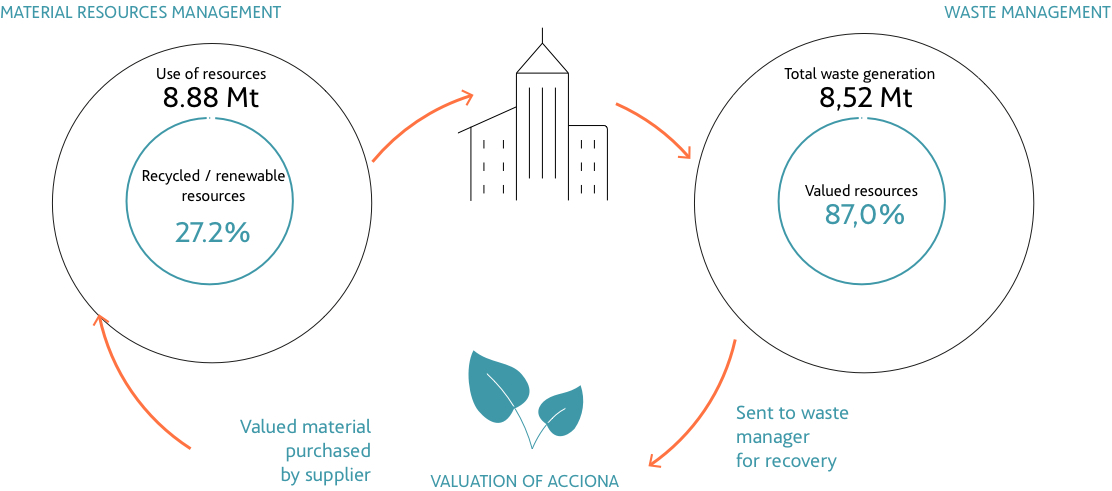
- 93% of CapEx aligned with sustainable activities according to European taxonomy.
- Voluntary planting of 74.947 trees.
- 24% reduction in the amount of waste sent to landfill compared to 2020.
- Consumption of 27% of recycled or renewable raw materials and material resources.
- Adoption of a new circular economy policy.
KEY CHALLENGES 2022
- Reduce GHG emissions by 23.08% (scopes 1 and 2) and 18.08% (scope 3*) compared to 2017, in line with the 2030 SBT target of 1.5°C reduction, and offset GHG emissions from its direct operations
- Invest 90% of CapEx in sustainable activities according to European taxonomy
- > Carry out voluntary planting of 232,500 trees.
- Reduce the amount of waste going to landfill by 20% by 2020
- Achieve 14% consumption of resources from renewable or recycled sources.
- Reduce surface, ground and municipal water consumption by 11% in water-stressed areas by 2020.
Changes in relevant indicators of the SMP 2025
| 2020 | 2021 | 2020-2021 Variation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CapEx aligned with the European taxonomy of sustainable activities (%)* | 85 % | 93 % | + 8.0 pp |
| GHG emissions Scope 1+2 (million tCO2e) | 0.13 | 0.17 | + 31 % |
| Share of renewable and recycled resources (%) | 10 | 27 | + 17 pb |
| Percentage of waste sent to landfill (%) | 23 | 13 | - 10 pb |
| Total water consumption (hm3) | 4.7 | 5.0 | + 6.4 % |
CLIMATE
ACCIONA promotes the adoption of ambitious global objectives regarding the decarbonization of the economy to integrate the management of climate change risks and opportunities into its model. This is reported in accordance with the European Commission's climate reporting guidance and the recommendations of the Financial Stability Board, through its Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD).
Preventing emissions
At the end of 2021, ACCIONA had 11,245 MW of installed renewable capacity, having generated 24,541 GWh. This renewable production prevented the emission of 13.4 million tons of CO2 e, 11,209 tNOx, 32,377 tSOx and 264 tPM 10 into the atmosphere.
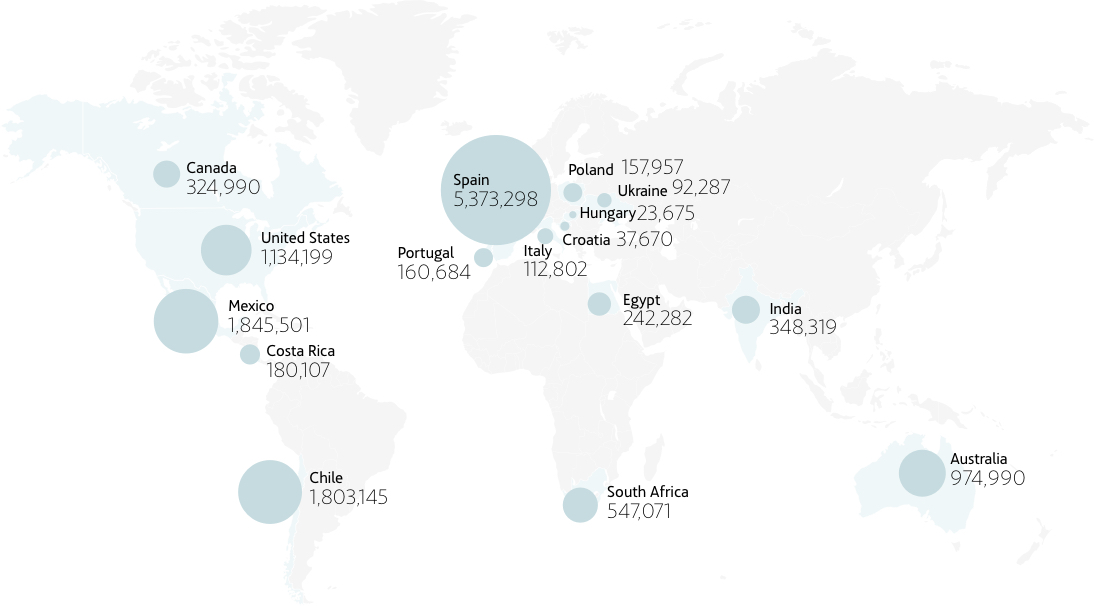
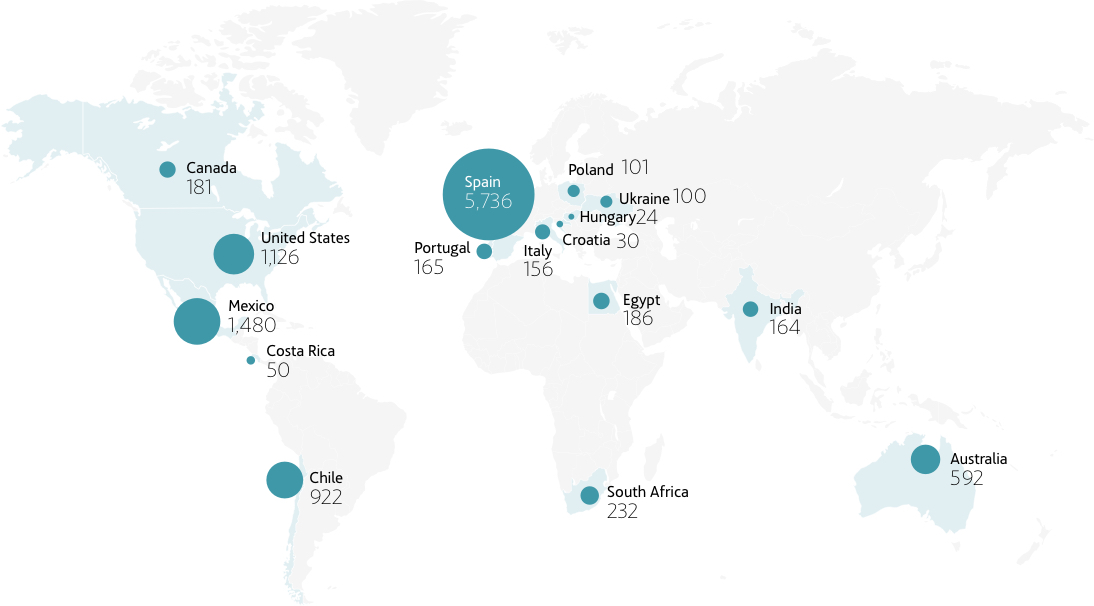
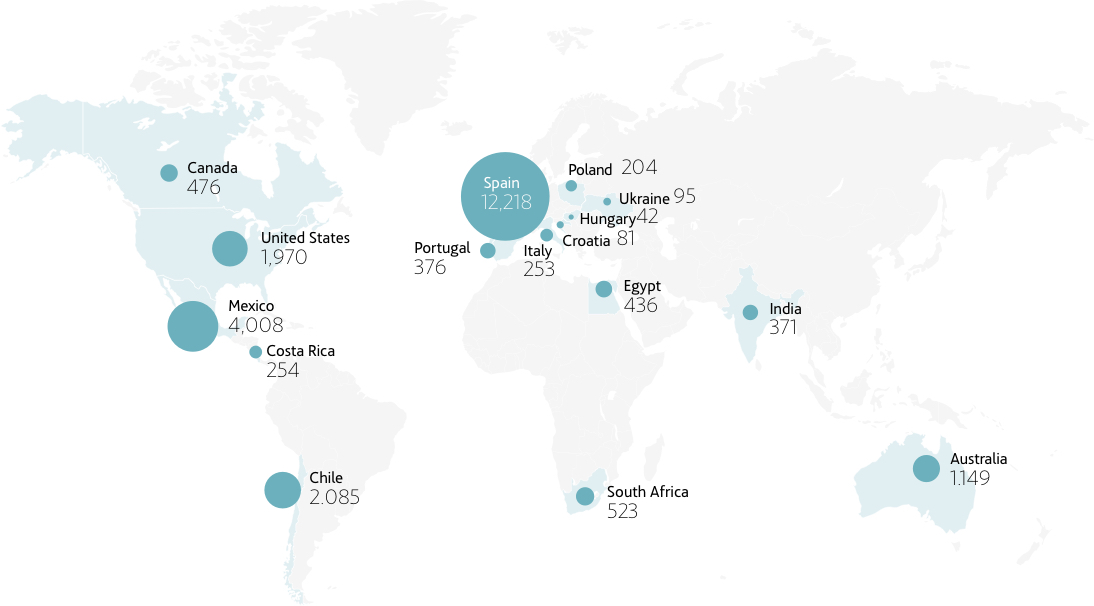
WATER
ACCIONA's water agenda is determined by strict compliance with legislation, responsible and efficient management, the establishment of specific objectives through its Sustainability Master Plan, the development of new technologies, the integration of water into risk management, the extension of its principles to the value chain and transparent communication.
ACCIONA carries out 3 different uses of water in the scope of its activities:
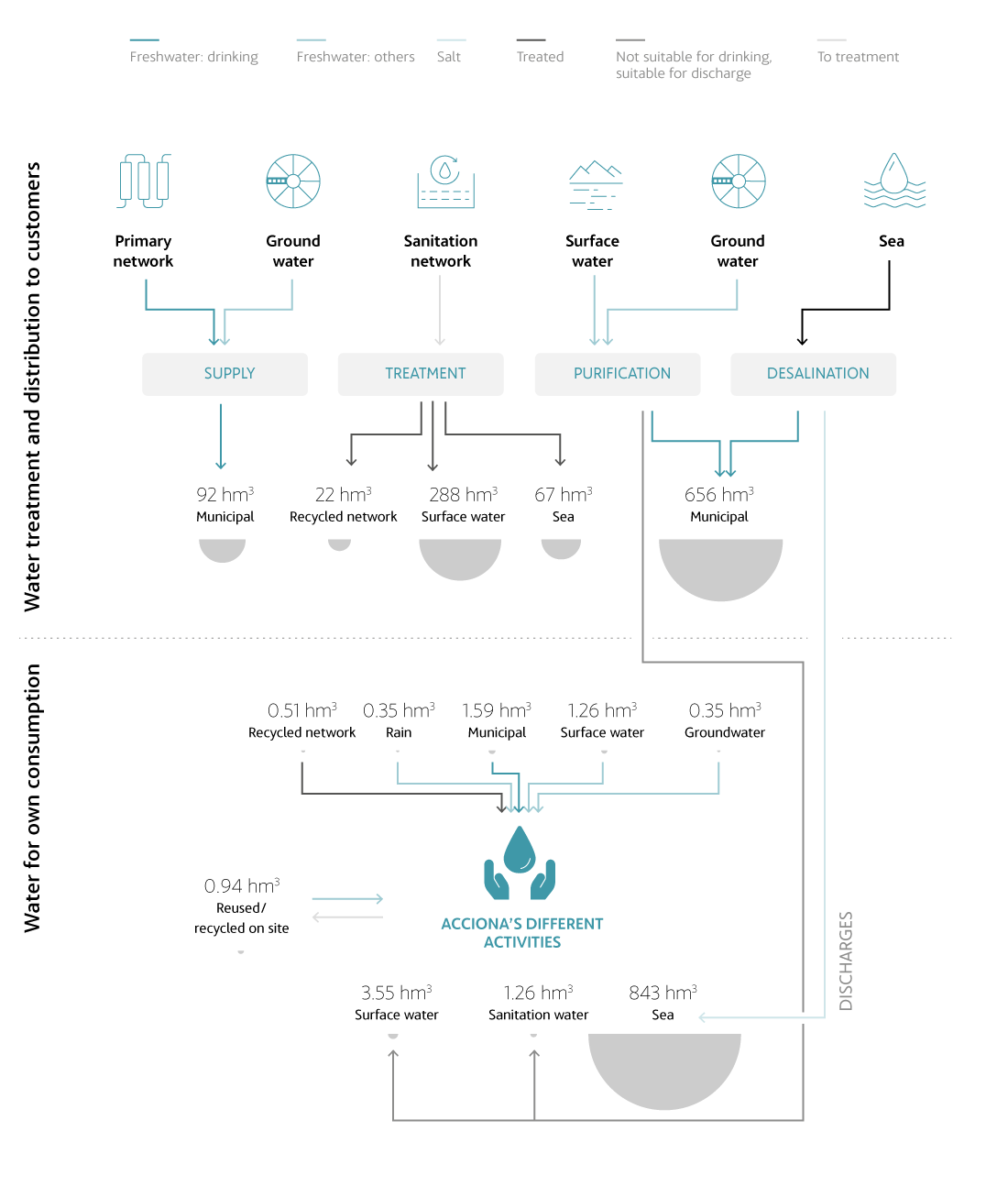
- Treatment and distribution of water for customers: this is water collected at desalination plants, drinking water treatment plants, wastewater treatment plants or supply services operated by the company to meet the demand of its customers.
- Water for own consumption: water intended for consumption in the company's facilities.
- Discharges: the remaining water for consumption that has not been evaporated or incorporated into any of the company's assets, and which leaves its facilities as specified in the corresponding discharge authorizations.
Treatment and consumption of water
CIRCULAR ECONOMY
Since 2021, ACCIONA has had a circular economy policy aimed at developing projects without using virgin materials or fossil fuels, without generating waste and while regenerating the environment. ACCIONA carries out multiple actions that demonstrate its performance in this area:
- It generates renewable energy from inexhaustible sources such as the sun or wind and from agricultural and/or forestry waste.
- It produces drinking water from seawater in water-stressed regions using the best available techniques with a view to reducing energy costs
- It develops infrastructure that improves transport efficiency, renewable energy generation and distribution, waste management and the sustainability of cities.
- It provides shared electric mobility services, infrastructure maintenance, energy management and segregated waste collection, as well as waste transport, sorting and recovery.
ACCIONA also optimizes the circularity of its processes as follows:
- It uses life cycle analysis tools (7 LCAs carried out in 2021) to assess and reduce the impact of its developments, as well as its material and energy consumption
- Minimizes your fossil fuel energy consumption.
- Rationalizes its water consumption and uses alternative water sources that do not deplete existing resources
- It provides a second life for waste and by-products derived from its processes, such as soil, rubble, ash, slag, vegetable waste or sewage sludge.
- Maximizes the usefulness of materials and uses sustainable resources such as recycled aggregates, renewable resources such as FSC-certified wood and biomass, or advanced resources such as composites, which minimize the amount of components used.
- It carries out intense R&D&I work in all areas of its activity, improving the efficiency of its processes and the performance of the resources used
- It uses digitalization as a catalyst for circular opportunities in construction, whether through technologies such as building information modelling, machine automation or 3D printing.
- It works closely with its stakeholders on training and awareness-raising on the circular economy.
MATERIAL FLOWS AT ACCIONA
BIODIVERSITY
For Acciona, the conservation of biodiversity and the responsible use of natural heritage are, in addition to an ethical commitment, essential to ensure global sustainability. ACCIONA has a specific corporate biodiversity policy that promotes, through various principles, the appreciation and conservation of animal and plant species as necessary means to ensure economic development and social progress.
In its new Sustainability Master Plan 2025, ACCIONA has included a strategic line on biodiversity, with the aim of both applying the impact mitigation hierarchy in all its projects and setting targets that can generate a positive material impact on the environment and biodiversity through solutions based on the science of nature.
Mitigation hierarchy scheme
00
Impact
Initial biodiversity impact
01
Prevention
Residual biodiversity impact
02
Minimization
03
Restoration
04
Compensation
Additional benefits
Equivalent compensation
Zero net loss
Net income
Most significant environmental impacts by area
INTEGRATED ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
In 2021, 82 projects promoted by ACCIONA have undergone an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA). Of these, 15 have already obtained favorable environmental impact statements. ACCIONA has also monitored 298 Environmental Monitoring Plans (EMP) at centers and facilities under construction, operation and/or maintenance.
ACCIONA's environmental management systems are verified and certified by independent accredited entities, in accordance with the international ISO 14001 standard. The management model is based on the following elements:
- Identification, evaluation and minimization of environmental alterations that may be caused during the development of the company's activities
- Environmental risk analysis through a regulated technical procedure that measures the risk of an accident damaging the environment or, on the contrary, a negative environmental impact on ACCIONA's activity.
- Identification and verification of legal requirements through the use of specific tools, which enable the management of compliance with administrative obligations and other commitments upheld, in addition to those required by law.
- Operational control by means of corporate tools that collect quantitative environmental information from each center, making it possible to manage the evolution of processes, set objectives and define strategies.
- Recording and classification of near-environmental accidents.
- Implementation of tools for continuous improvement, identification and dissemination of lessons learned and good practices.
- Setting out annual environmental objectives in all businesses, taking as a reference the most significant aspects linked to the environment in the management systems and the PDS.
 2021 Report
2021 Report